Top 5
The banking sector has often demonstrated resilience in the wake of devastating crises. However, in 2020, a year characterised by the COVID-19 pandemic, it is about survival. With profits on the decline, non-performing loans on the rise and return on equity plunging, banks are focusing on weathering the crisis in the immediate future. In the medium and long term, strategy is being anchored on adaptation with digital transformation at the core. This is based on the fact that COVID-19 has defined a ‘new normal’.
For CIMB Niaga Bank, Indonesia’s second largest privately owned bank by assets, the situation is no different. The need to withstand the impacts of the pandemic is paramount. But the bank has not shifted focus from its Forward 23+ strategy centred on customer journey, digitalisation, enhancing productivity and finding new opportunities. The strategy, which is part of the larger CIMB Group plan, is designed to ensure CIMB Niaga joins the rank of top banks in the ASEAN region.

Due to this ambition, CIMB Niaga Bank, which is majority owned by the Malaysia-based CIMB Group, is strategically positioned to support clients and businesses suffering from the disruptions that have been forced on the banking sector by COVID-19. The bank has a strong footing. It has been in operation for over 65 years. It boasts a wide-range of banking products and services, both conventional and Sharia. With a network of 390 branches, 34 digital lounges and 27 mobile branches, the bank has over 12,000 employees.
CIMB Niaga intends to weather the challenges brought upon us by the pandemic from this firm foundation, but also aims to anchor future growth. This is critical, and for good reason. Indonesia, Southeast Asia’s largest economy, is among the countries that have been badly affected by the pandemic, both directly and indirectly. At the end of November 2020, the country had 522,581 COVID-19 confirmed cases with 16,521 deaths. Economically, the impacts have been severe, forcing the country into a recession. The last time this happened was during the 1998 Asian financial crisis.
Since 2014, Indonesia’s gross domestic growth has averaged five percent per year, ranking it among the fastest expanding nations. This year, however, most sectors of the economy including transportation and warehousing, financial services, manufacturing, tourism, construction, mining and construction are on a downward spiral. The wider effect is that Indonesia is headed for negative growth this year. Worse still, the World Bank is projecting an “uneven and volatile” recovery in the coming years.
As the heartbeat of businesses, the banking sector is feeling the devastating effects of the pandemic. In the period ending September 30, 2020, the seven top banks in Indonesia posted an average decline in profitability of 29.7 percent. This is in line with the country’s Financial Services Authority (FSA) revised forecast, indicating that profits would decline by around 30 to 40 percent on average in 2020.
Robust fiscal planning
Amid the tough operating environment, CIMB Niaga continues to demonstrate a spirit of community and strength. For the bank, most indicators remain strong with liquidity, asset quality and cost management being central in the bank’s ability to withstand the current crisis. This is reflected in the financial results for the nine-month period leading up to September 30th. During this period, CIMB Niaga’s capital adequacy ratio remained strong at 20.8 percent while total assets stood at IDR 281.7tr ($15.4bn). This ensured the bank maintained its position as Indonesia’s second largest privately owned bank by assets.
While the performance of the conventional bank remains solid, CIMB Niaga Sharia maintained its position as the largest Islamic business unit in Indonesia. The unit’s total financing was valued at IDR 32.6tr ($2.3bn) with deposits increasing to IDR 35.1tr ($2.4bn). Notably, CIMB Niaga is one of the Sharia banks that has embraced digitisation. This enables the bank to support the burgeoning needs for quality Sharia-based products in a country that is predominantly Islamic.
In Indonesia, the FSA has predicted a muted growth in loans and advances. But this has not stopped CIMB Niaga amassing a strong loan book that stands at IDR 180.9tr ($12.8bn), contributed to by a 4.1 percent year-on-year growth in the consumer-banking segment. Total deposits, on the other hand, stood at IDR 211.9tr ($15bn). During the period, the bank posted a net profit of IDR 1.9tr ($134.5m). Although the net profits were 31 percent lower compared to the IRD 2.6tr ($184m) realised in 2019, they represented the bank’s determination to navigate the crisis. This is evident on many fronts. Despite the pandemic having widespread disruptive effects, particularly on service delivery, CIMB Niaga has actively responded with digital transformation being central to ensuring business continuity. In fact, COVID-19 did not bring about the need for digitisation for CIMB Niaga. The bank, which was established in 1955 under the name Bank Niaga, was founded on innovation and a forward-thinking philosophy.
Years in the making
CIMB Niaga was the first bank in Indonesia to install an automated teller machine (ATM) and to launch a mobile-phone eWallet. In 2017, the bank correctly predicted that the banking sector in the country was ripe for accelerated digital revolution. To be a leader on the digital frontier, the bank deployed significant resources to roll out an ambitious strategy that is redefining service delivery in the midst of the pandemic. For most banks, the digital transformation has been a necessary evil brought about by COVID-19. For CIMB Niaga, however, it is a well-thought-out business strategy. As the bank delivers the enhancement on digital channels, it has always remained passionate and curious about new and powerful methods. This includes the ‘design first’ thinking process that challenges the status quo and invents new ways of doing things, as well as agile methodologies that speed up project and features delivery.
Other methods include constant benchmarking and learning from competitors, cutting across local, regional and international boundaries, conducting surveys to discover more about the customer and being true to the Kaizen concept of constant and never-ending improvements. The results of the conscious approach to digitisation have been significant in avoiding service disruption especially considering Indonesia has witnessed major lockdowns to contain the spread of the disease.
To start with, CIMB Niaga has been able to leverage the COVID-19 pandemic as an opportunity to seamlessly redirect customers to digital channels like OCTO mobile and OCTO Clicks online banking. It has also encouraged customers to utilise its payment capabilities and cashless transactions. These include QR transactions that allow customers to transact without cards, and also our OCTO vending machines distributed to key locations across Indonesia. With adoption of online platforms to interact with customers, the bank has been able to reach more customers.
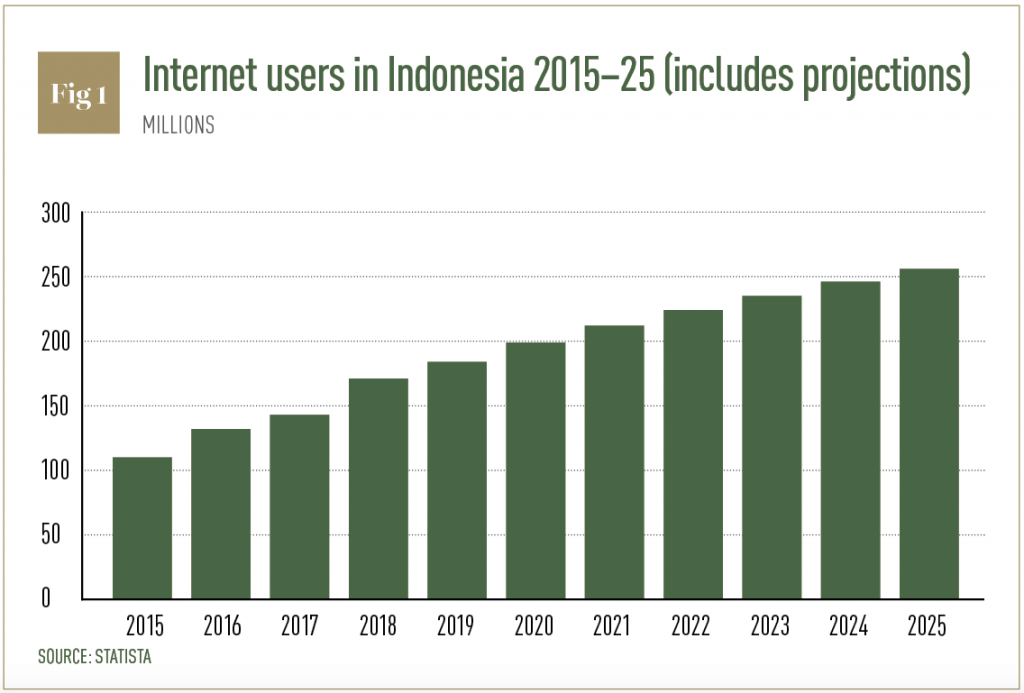
In fact, the platforms have been ideal considering the geographical perspective of Indonesia, a country that consists of many islands. More importantly though is the fact that CIMB Niaga is at the forefront of the country, in terms of playing a central role in the projected e-commerce explosion. Numerous surveys show the online economy and e-commerce could reach $35bn this year, up from $23bn in 2019, and is on track to cross the $130bn mark by 2025.
Internally, adoption of digital channels by CIMB Niaga customers has been swift. The bank is recording higher penetration rates on mobile banking, something that is reflected by a significant increase in digital transactions that are in excess of 96 percent of the total yearly transactions processed by the bank. Financial transactions have also increased by almost 50 percent while active users have also grown significantly (see Fig 1).
Pushing things forward
The bank has more ambitious 2021 targets due to the robust growth seen. Over the next 12 to 24 months, CIMB Niaga will be focusing on perfecting its digital bank capabilities and strengthening its foothold expansion to be a truly digital bank. Already, it has implemented several exciting initiatives. These include a digital OCTO savings account and credit card set for launch next year. Concurrently, a team is working on building the initial frameworks to continue the expansion to a more robust app for its mobile banking. This year alone, the team will have delivered over 74 features on mobile, providing more conveniences and solutions to users. Of importance though, is that CIMB Niaga is putting security at the core of its digital networks.
On this, the bank is not only compliant to industry standards but has systems to monitor, detect and prevent fraud. Its OCTO mobile policy implemented in 2017 has, for instance, reduced cases of fraud to record low levels. For CIMB Niaga, the vision to venture into the digital space was a masterstroke. This is because as COVID-19 forces other banks to accelerate the digital transformation, CIMB Niaga has already responded to customer needs. But even as it continues to roll out innovations and solutions that conveniently bridge financial and everyday life for users, the bank is cognizant of the fact that it cannot afford to lock out conservative customers who still believe in bricks and mortar.
Notably, branches will still be available for this type of customer. However, the fact that the numbers are on a decline has seen CIMB Niaga proactively continue educating customers on its digital capabilities and conveniences. The result has been faster transition into the digital space. For customers who are perhaps more apprehensive, the bank’s relationship managers are well versed in digital onboarding. This makes them ready to assist clients when they feel comfortable and ready to turn to digital.